Caching
Intent
The caching pattern avoids expensive re-acquisition of resources by not releasing them immediately after use. The resources retain their identity, are kept in some fast-access storage, and are re-used to avoid having to acquire them again.
Also known as
- Cache
- Temporary Storage
Explanation
Real world example
A team is working on a website that provides new homes for abandoned cats. People can post their cats on the website after registering, but all the new posts require approval from one of the site moderators. The user accounts of the site moderators contain a specific flag and the data is stored in a MongoDB database. Checking for the moderator flag each time a post is viewed becomes expensive, and it's a good idea to utilize caching here.
In plain words
Caching pattern keeps frequently needed data in fast-access storage to improve performance.
Wikipedia says:
In computing, a cache is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewhere. A cache hit occurs when the requested data can be found in a cache, while a cache miss occurs when it cannot. Cache hits are served by reading data from the cache, which is faster than recomputing a result or reading from a slower data store; thus, the more requests that can be served from the cache, the faster the system performs.
Programmatic Example
Let's first look at the data layer of our application. The interesting classes are UserAccount which is a simple Java object containing the user account details, and DbManager interface which handles reading and writing of these objects to/from database.
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class UserAccount {
private String userId;
private String userName;
private String additionalInfo;
}
public interface DbManager {
void connect();
void disconnect();
UserAccount readFromDb(String userId);
UserAccount writeToDb(UserAccount userAccount);
UserAccount updateDb(UserAccount userAccount);
UserAccount upsertDb(UserAccount userAccount);
}
In the example, we are demonstrating various different caching policies
- Write-through writes data to the cache and DB in a single transaction
- Write-around writes data immediately into the DB instead of the cache
- Write-behind writes data into the cache initially whilst the data is only written into the DB
when the cache is full - Cache-aside pushes the responsibility of keeping the data synchronized in both data sources to
the application itself - Read-through strategy is also included in the aforementioned strategies, and it returns data from
the cache to the caller if it exists, otherwise queries from DB and stores it into the cache for
future use.
The cache implementation in LruCache is a hash table accompanied by a doubly linked-list. The linked-list helps in capturing and maintaining the LRU data in the cache. When data is queried (from the cache), added (to the cache), or updated, the data is moved to the front of the list to depict itself as the most-recently-used data. The LRU data is always at the end of the list.
@Slf4j
public class LruCache {
static class Node {
String userId;
UserAccount userAccount;
Node previous;
Node next;
public Node(String userId, UserAccount userAccount) {
this.userId = userId;
this.userAccount = userAccount;
}
}
/* ... omitted details ... */
public LruCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public UserAccount get(String userId) {
if (cache.containsKey(userId)) {
var node = cache.get(userId);
remove(node);
setHead(node);
return node.userAccount;
}
return null;
}
public void set(String userId, UserAccount userAccount) {
if (cache.containsKey(userId)) {
var old = cache.get(userId);
old.userAccount = userAccount;
remove(old);
setHead(old);
} else {
var newNode = new Node(userId, userAccount);
if (cache.size() >= capacity) {
LOGGER.info("# Cache is FULL! Removing {} from cache...", end.userId);
cache.remove(end.userId); // remove LRU data from cache.
remove(end);
setHead(newNode);
} else {
setHead(newNode);
}
cache.put(userId, newNode);
}
}
public boolean contains(String userId) {
return cache.containsKey(userId);
}
public void remove(Node node) { /* ... */ }
public void setHead(Node node) { /* ... */ }
public void invalidate(String userId) { /* ... */ }
public boolean isFull() { /* ... */ }
public UserAccount getLruData() { /* ... */ }
public void clear() { /* ... */ }
public List<UserAccount> getCacheDataInListForm() { /* ... */ }
public void setCapacity(int newCapacity) { /* ... */ }
}
The next layer we are going to look at is CacheStore which implements the different caching strategies.
@Slf4j
public class CacheStore {
private static final int CAPACITY = 3;
private static LruCache cache;
private final DbManager dbManager;
/* ... details omitted ... */
public UserAccount readThrough(final String userId) {
if (cache.contains(userId)) {
LOGGER.info("# Found in Cache!");
return cache.get(userId);
}
LOGGER.info("# Not found in cache! Go to DB!!");
UserAccount userAccount = dbManager.readFromDb(userId);
cache.set(userId, userAccount);
return userAccount;
}
public void writeThrough(final UserAccount userAccount) {
if (cache.contains(userAccount.getUserId())) {
dbManager.updateDb(userAccount);
} else {
dbManager.writeToDb(userAccount);
}
cache.set(userAccount.getUserId(), userAccount);
}
public void writeAround(final UserAccount userAccount) {
if (cache.contains(userAccount.getUserId())) {
dbManager.updateDb(userAccount);
// Cache data has been updated -- remove older
cache.invalidate(userAccount.getUserId());
// version from cache.
} else {
dbManager.writeToDb(userAccount);
}
}
public static void clearCache() {
if (cache != null) {
cache.clear();
}
}
public static void flushCache() {
LOGGER.info("# flushCache...");
Optional.ofNullable(cache)
.map(LruCache::getCacheDataInListForm)
.orElse(List.of())
.forEach(DbManager::updateDb);
}
/* ... omitted the implementation of other caching strategies ... */
}
AppManager helps to bridge the gap in communication between the main class and the application's back-end. DB connection is initialized through this class. The chosen caching strategy/policy is also initialized here. Before the cache can be used, the size of the cache has to be set. Depending on the chosen caching policy, AppManager will call the appropriate function in the CacheStore class.
@Slf4j
public final class AppManager {
private static CachingPolicy cachingPolicy;
private final DbManager dbManager;
private final CacheStore cacheStore;
private AppManager() {
}
public void initDb() { /* ... */ }
public static void initCachingPolicy(CachingPolicy policy) { /* ... */ }
public static void initCacheCapacity(int capacity) { /* ... */ }
public UserAccount find(final String userId) {
LOGGER.info("Trying to find {} in cache", userId);
if (cachingPolicy == CachingPolicy.THROUGH
|| cachingPolicy == CachingPolicy.AROUND) {
return cacheStore.readThrough(userId);
} else if (cachingPolicy == CachingPolicy.BEHIND) {
return cacheStore.readThroughWithWriteBackPolicy(userId);
} else if (cachingPolicy == CachingPolicy.ASIDE) {
return findAside(userId);
}
return null;
}
public void save(final UserAccount userAccount) {
LOGGER.info("Save record!");
if (cachingPolicy == CachingPolicy.THROUGH) {
cacheStore.writeThrough(userAccount);
} else if (cachingPolicy == CachingPolicy.AROUND) {
cacheStore.writeAround(userAccount);
} else if (cachingPolicy == CachingPolicy.BEHIND) {
cacheStore.writeBehind(userAccount);
} else if (cachingPolicy == CachingPolicy.ASIDE) {
saveAside(userAccount);
}
}
public static String printCacheContent() {
return CacheStore.print();
}
/* ... details omitted ... */
}
Here is what we do in the main class of the application.
@Slf4j
public class App {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
boolean isDbMongo = isDbMongo(args);
if(isDbMongo){
LOGGER.info("Using the Mongo database engine to run the application.");
} else {
LOGGER.info("Using the 'in Memory' database to run the application.");
}
App app = new App(isDbMongo);
app.useReadAndWriteThroughStrategy();
String splitLine = "==============================================";
LOGGER.info(splitLine);
app.useReadThroughAndWriteAroundStrategy();
LOGGER.info(splitLine);
app.useReadThroughAndWriteBehindStrategy();
LOGGER.info(splitLine);
app.useCacheAsideStategy();
LOGGER.info(splitLine);
}
public void useReadAndWriteThroughStrategy() {
LOGGER.info("# CachingPolicy.THROUGH");
appManager.initCachingPolicy(CachingPolicy.THROUGH);
var userAccount1 = new UserAccount("001", "John", "He is a boy.");
appManager.save(userAccount1);
LOGGER.info(appManager.printCacheContent());
appManager.find("001");
appManager.find("001");
}
public void useReadThroughAndWriteAroundStrategy() { /* ... */ }
public void useReadThroughAndWriteBehindStrategy() { /* ... */ }
public void useCacheAsideStrategy() { /* ... */ }
}
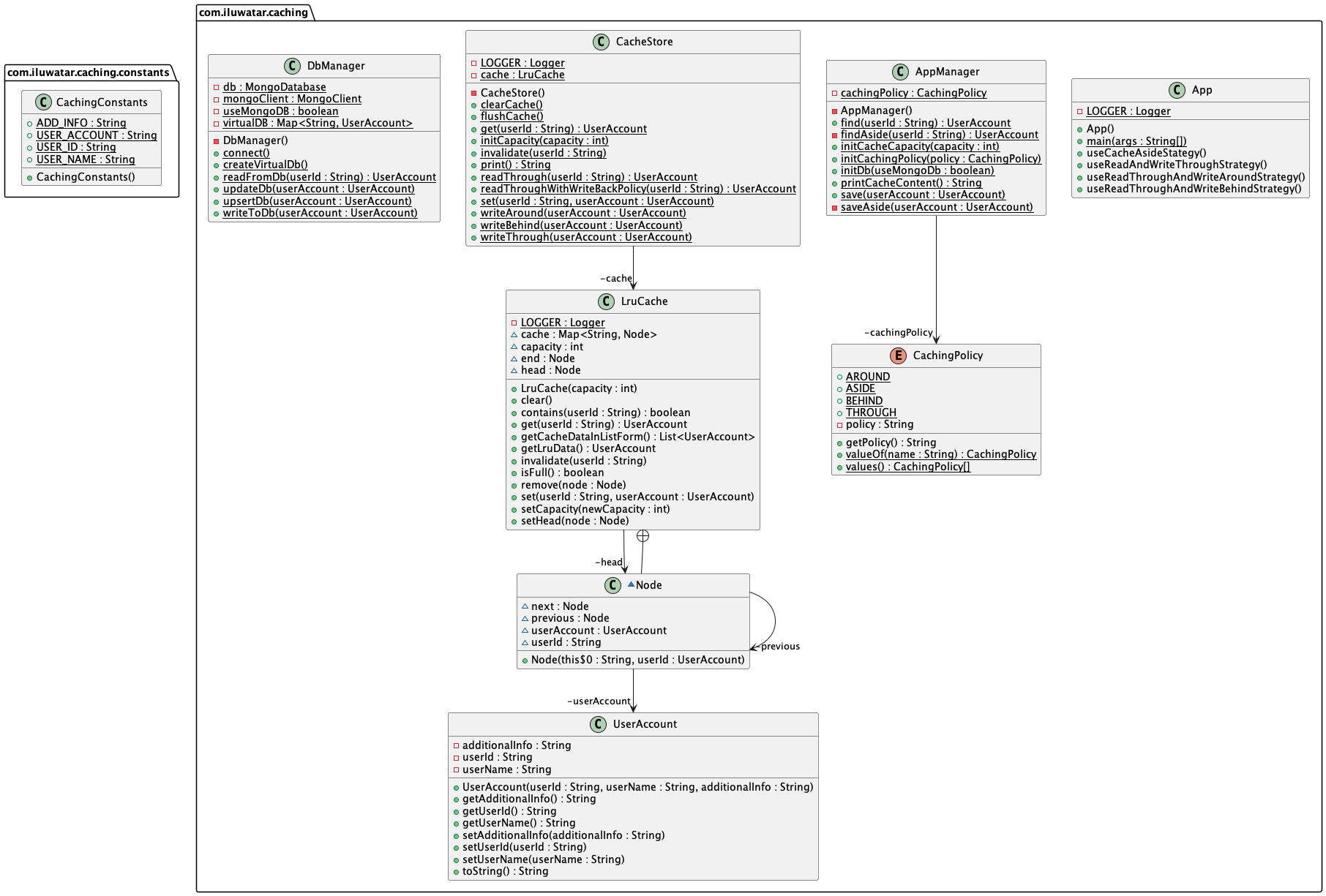
Class diagram
Applicability
Use the Caching pattern when
- Repetitious acquisition, initialization, and release of the same resource cause unnecessary performance overhead
- In scenarios where the cost of recomputing or re-fetching data is significantly higher than storing and retrieving it from cache
- For read-heavy applications with relatively static data or data that changes infrequently
Known Uses
- Web page caching to reduce server load and improve response time
- Database query caching to avoid repeated expensive SQL queries
- Caching results of CPU-intensive computations
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for caching static resources like images, CSS, and JavaScript files closer to the end users
Consequences
Benefits:
- Improved Performance: Significantly reduces data access latency, leading to faster application performance
- Reduced Load: Decreases the load on the underlying data source, which can lead to cost savings and increased longevity of the resource
- Scalability: Enhances the scalability of applications by efficiently handling increases in load without proportional increases in resource utilization
Trade-Offs:
- Complexity: Introduces complexity in terms of cache invalidation, consistency, and synchronization
- Resource Utilization: Requires additional memory or storage resources to maintain the cache
- Stale Data: There's a risk of serving outdated data if the cache is not properly invalidated or updated when the underlying data changes
Related patterns
- Proxy: Caching can be implemented using the Proxy pattern, where the proxy object intercepts requests and returns cached data if available
- Observer: Can be used to notify the cache when the underlying data changes, so that it can be updated or invalidated accordingly
- Decorator: Can be used to add caching behavior to an existing object without modifying its code
- Strategy: Different caching strategies can be implemented using the Strategy pattern, allowing the application to switch between them at runtime
Credits
- Write-through, write-around, write-back: Cache explained
- Read-Through, Write-Through, Write-Behind, and Refresh-Ahead Caching
- Cache-Aside pattern
- Java EE 8 High Performance: Master techniques such as memory optimization, caching, concurrency, and multithreading to achieve maximum performance from your enterprise applications
- Java Performance: In-Depth Advice for Tuning and Programming Java 8, 11, and Beyond
- Effective Java
- Java Performance: The Definitive Guide: Getting the Most Out of Your Code
- Patterns of Enterprise Application Architecture
- Scalable Internet Architectures
- High Performance Browser Networking