Serialized Entity Pattern
Intent
To easily persist Java objects to the database.
Explanation
Java serialization allow us to convert the object to a set of bytes. We can store these bytes into database as
BLOB(binary long objects) and read them at any time and reconstruct them into Java objects.
Programmatic Example
Walking through our customers example, here's the basic Customer entity.
@Getter
@Setter
@EqualsAndHashCode
@ToString
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Country implements Serializable {
private int code;
private String name;
private String continents;
private String language;
public static final long serialVersionUID = 7149851;
// Constructor ->
// getters and setters ->
}
Here is CountrySchemaSql, this class have method allow us to serialize Country object and insert it into the
database, also have a method that read serialized data from the database and deserialize it to Country object.
@Slf4j
public class CountrySchemaSql {
public static final String CREATE_SCHEMA_SQL = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS WORLD (ID INT PRIMARY KEY, COUNTRY BLOB)";
public static final String DELETE_SCHEMA_SQL = "DROP TABLE WORLD IF EXISTS";
private Country country;
private DataSource dataSource;
/**
* Public constructor.
*
* @param dataSource datasource
* @param country country
*/
public CountrySchemaSql(Country country, DataSource dataSource) {
this.country = new Country(
country.getCode(),
country.getName(),
country.getContinents(),
country.getLanguage()
);
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
/**
* This method will serialize a Country object and store it to database.
* @return int type, if successfully insert a serialized object to database then return country code, else return -1.
* @throws IOException if any.
*/
public int insertCountry() throws IOException {
var sql = "INSERT INTO WORLD (ID, COUNTRY) VALUES (?, ?)";
try (var connection = dataSource.getConnection();
var preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oss = new ObjectOutputStream(baos)) {
oss.writeObject(country);
oss.flush();
preparedStatement.setInt(1, country.getCode());
preparedStatement.setBlob(2, new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray()));
preparedStatement.execute();
return country.getCode();
} catch (SQLException e) {
LOGGER.info("Exception thrown " + e.getMessage());
}
return -1;
}
/**
* This method will select a data item from database and deserialize it.
* @return int type, if successfully select and deserialized object from database then return country code,
* else return -1.
* @throws IOException if any.
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if any.
*/
public int selectCountry() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
var sql = "SELECT ID, COUNTRY FROM WORLD WHERE ID = ?";
try (var connection = dataSource.getConnection();
var preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql)) {
preparedStatement.setInt(1, country.getCode());
try (ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery()) {
if (rs.next()) {
Blob countryBlob = rs.getBlob("country");
ByteArrayInputStream baos = new ByteArrayInputStream(countryBlob.getBytes(1, (int) countryBlob.length()));
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(baos);
country = (Country) ois.readObject();
LOGGER.info("Country: " + country);
}
return rs.getInt("id");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
LOGGER.info("Exception thrown " + e.getMessage());
}
return -1;
}
}
This App.java will first delete a World table from the h2 database(if there is one) and create a new table calledWORLD to ensure we have a table we want.
It will then create two Country objects called China and UnitedArabEmirates, then create two CountrySchemaSql
objects and use objects China and UnitedArabEmirates as arguments.
Finally, call SerializedChina.insertCountry() and serializedUnitedArabEmirates.insertCountry() to serialize and
store them to database, and call SerializedChina.selectCountry() and serializedUnitedArabEmirates.selectCountry()
methods to read and deserialize data items to Country objects.
@Slf4j
public class App {
private static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:h2:mem:testdb;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1";
private App() {
}
/**
* Program entry point.
* @param args command line args.
* @throws IOException if any
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if any
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
final var dataSource = createDataSource();
deleteSchema(dataSource);
createSchema(dataSource);
final var China = new Country(
86,
"China",
"Asia",
"Chinese"
);
final var UnitedArabEmirates = new Country(
971,
"United Arab Emirates",
"Asia",
"Arabic"
);
final var serializedChina = new CountrySchemaSql(China, dataSource);
final var serializedUnitedArabEmirates = new CountrySchemaSql(UnitedArabEmirates, dataSource);
serializedChina.insertCountry();
serializedUnitedArabEmirates.insertCountry();
serializedChina.selectCountry();
serializedUnitedArabEmirates.selectCountry();
}
private static void deleteSchema(DataSource dataSource) {
try (var connection = dataSource.getConnection();
var statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.execute(CountrySchemaSql.DELETE_SCHEMA_SQL);
} catch (SQLException e) {
LOGGER.info("Exception thrown " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private static void createSchema(DataSource dataSource) {
try (var connection = dataSource.getConnection();
var statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.execute(CountrySchemaSql.CREATE_SCHEMA_SQL);
} catch (SQLException e) {
LOGGER.info("Exception thrown " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private static DataSource createDataSource() {
var dataSource = new JdbcDataSource();
dataSource.setURL(DB_URL);
return dataSource;
}
}
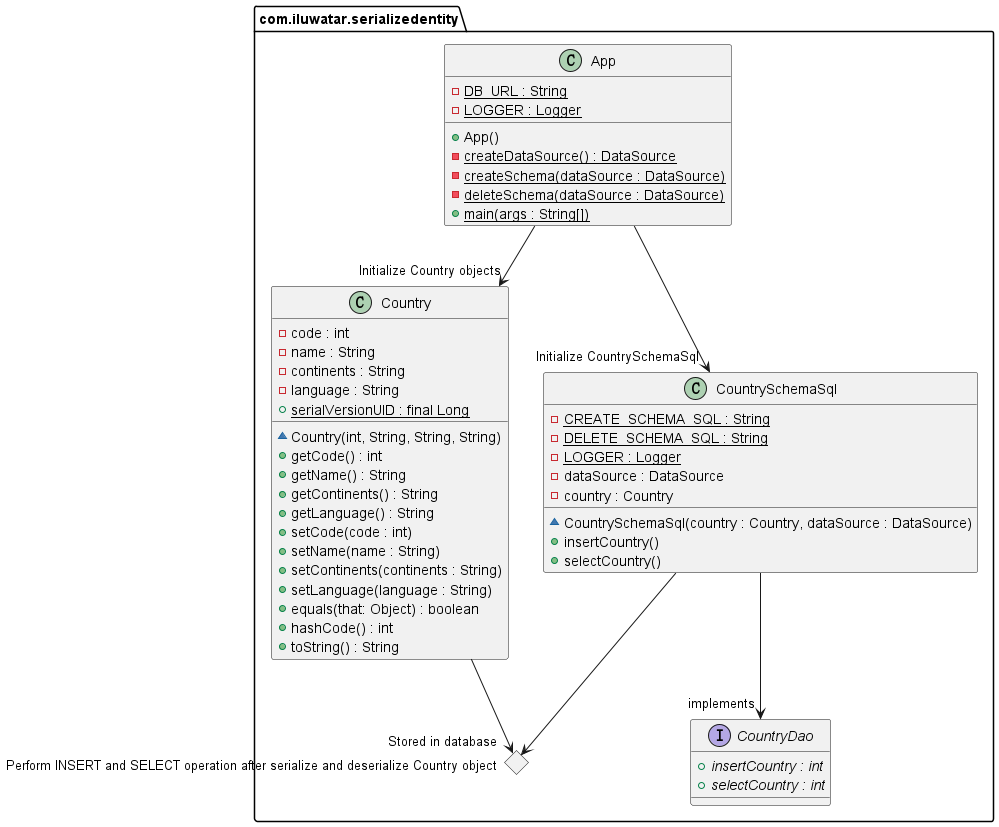
Class diagram
Applicability
Use the Serialized Entity pattern when
- You want to easily persist Java objects to the database.
Related patterns
Credits
- J2EE Design Patterns by William Crawford, Jonathan Kaplan
- komminen (His attempts of serialized-entity inspired me and learned a lot from his code)